| Previous
Page |
PCLinuxOS
Magazine |
PCLinuxOS |
Article List |
Disclaimer |
Next Page |
Short Topix: Google May Have Invented Time Crystals |
|
by Paul Arnote (parnote)
  All across the globe, internet users have noticed an explosion of billboards advertising the DuckDuckGo search engine. See the two pictures above as examples. At a time when internet privacy is under increasing attack, DuckDuckGo (DDG) is making a push to get its name out in front of more and more users. Those who are already concerned about internet privacy already know about DDG and how it anonymizes search data so that none of your personal information is collected, and how it doesn't track you across your internet travels. So, just how does DDG make money from its search engine? Easily enough, that answer can be found on a DDG Q&A web page, called "What Is the Business Model for DuckDuckGo?" Here is an excerpt from that DDG web page: DuckDuckGo has been a profitable company since 2014 without storing or sharing any personal information on people using our search engine. As we like to say, what you search on DuckDuckGo is private, even from us! We're proud to have a business model for a web-based business that's profitable without making your personal information the product. I'm happy to tell you all about how we make it work (and how other companies can, too). Though first, if you're not familiar with DuckDuckGo, we are an Internet privacy company that empowers you to seamlessly take control of your personal information online, without any tradeoffs. We operate a search engine alternative to Google at https://duckduckgo.com, and offer additional apps and extensions to protect you from Google, Facebook and other trackers, no matter where you go on the Internet. It's actually a big myth that search engines need to track your personal search history to make money or deliver quality search results. Almost all of the money search engines make (including Google) is based on the keywords you type in, without knowing anything about you, including your search history or the seemingly endless amounts of additional data points they have collected about registered and non-registered users alike. In fact, search advertisers buy search ads by bidding on keywords, not people. It makes intuitive sense, too. If you search for 'car', you are more likely to respond to a car ad than something you searched for last week. This keyword-based advertising is our primary business model. When you search on DuckDuckGo, we can show you an ad based on the keywords you type in. That's it. And it works. Our privacy policy, in a nutshell, is to not collect or share any personal information at all. Every time you search on DuckDuckGo it is as if you were there for the first time -- anonymous. It makes sense. So, why does Google persist in tracking you with your personal data? One word: greed. Quite some time ago, Google's greed overran their popular -- and former -- motto, "Do no evil." You can read more about it by visiting the DDG web page. I, for one, have changed to using DDG as my primary, "go to" search engine in all of my browsers that I use with any regularity. Admittedly, I haven't changed the default search engine to DDG in my browsers I don't use as often, but doing so is high on my list of "things to do" whenever I do use those browsers again. I suspect that as more is revealed about Google, its privacy invasions, its tracking, and other dubious information about the company too plentiful to list here, more people will be changing their preferred search engine. It took me a while, but once I switched, I haven't looked back, and I certainly haven't had any regrets. A Renewed Search For ET With A New Method  Illustrative photo of Galileo Galilei refracting through a telescope. (photo credit: THE GALILEO PROJECT) According to an article in the Jerusalem Post, a Harvard astronomer is proposing a newer way to search for ET. Instead of looking for radio waves and other signs of intelligent life as SETI does, Israeli scientist Prof. Avi Loeb of Harvard University's Astronomy Department is proposing the use of cameras and smaller telescopes to search for garbage. Loeb doesn't want to use warehouse-sized powerful telescopes. He asserts that their field of view is too narrow. Instead, he wants to use a network of smaller medium sized telescopes with a wide field of view, located in specific locations around the world, to scan for the "garbage" of intelligent civilizations. He claims that would be the "smoking gun" to verify that other extraterrestrial civilizations are, indeed, out there. His project is called the "Galileo Project," and could start amassing data as soon as 2023. In 2017, our solar system received its first interstellar visitor when the object dubbed Oumuamua (traveller in Hawaiian) cruised through our neighborhood. Scientists only really ever got to see much of Oumuamua as it was on its way out of our solar system, leaving many questions and much debate about it in its wake. Loeb contends that had his proposed system been in place when Oumuamua cruised by, many of the questions we have about it would have already been answered. Want To Protect Your Smartphone From Hackers? It's Easier Than You May Think.  Who better than the master hackers themselves -- the NSA -- for information on how to best protect your mobile devices from hackers. And, it's only two steps.
Step One: Turn your mobile device off. Do this at least once a week, and you will go a long, long way to preventing hackers from gaining access to your data, according to an article from the Associated Press. While there isn't much that can be done to totally thwart the efforts of hackers to gain access to the information and data stored on your mobile device, simply turning your phone off, then back on will make them work much, much harder to access that goldmine of information. If you make it harder for threat actors to access your information and data, there's a good chance they will move on to a much easier target who isn't as security minded. The NSA released a guide on best practices to safeguard or protect mobile devices last year. You can download it for free from here (PDF). The War On Your Privacy Monthly Update  THE NSA HAS WARNED ITS CONTRACTORS AND AFFILIATES TO AVOID using public wifi networks, as well as bluetooth and NFC connections in a public environment. Their guidelines represent a set of guidelines that represent "best use" practices. While aimed specifically at users who are involved in national security, members of the public would do well to also heed their advice. The NSA has published their recommendations/guidelines here (PDF), for all to see. T-MOBILE WAS RECENTLY HACKED, and the private information of up to 100 million users was gathered and made available for sale. Information from 30 million users was offered up by a hacker on an "underground forum" for the equivalent of $270,000 in BitCoin. The remainder of the customer data is being offered up for sale through private channels, according to an article on Engadget. THE NSA HAS AWARDED AMAZON A "SECRET" $10 BILLION CONTRACT to move some of its voluminous amounts of data to Amazon Web Services servers, according to an article on Nextgov. There are no reports of "privacy concerns," other than the fact that it involves the NSA, and that is NEVER a good combination any time you are talking about "privacy." A NEW ANDROID THREAT THAT RESEARCHERS CALL "FLYTRAP" is responsible for hijacking the Facebook accounts of over 10,000 users in 144 countries, according to an article on BleepingComputer.com. It uses a JavaScript injection to steal information, as well as the session cookies for a user's Facebook session. The malware threat actors use social engineering tricks -- like offering discount coupons for popular sites like NetFlix -- to trick people into clicking on the ad for the discount. When they click on the ad for the discount, the malware then proceeds to steal the Facebook session cookie, along with some other potentially sensitive data. Google May Have Invented Time Crystals  It's not very often we get to offer up praise for Google, so this feels a bit odd. According to an article on TheNextWeb (and widely reported on throughout many media outlets), a team of dozens of scientists working in partnership with Google's quantum computing labs, MAY have created the world's first time crystals. In doing so, they MAY have created a whole new phase of matter. I cannot EVEN BEGIN to explain the significance of time crystals and what they may mean. In fact, most of the rest of the world can't wrap their head around them, either. All I can tell you is that they can shift between different configurations, all without using or losing any energy. Go read the article on TheNextWeb by Tristan Greene. He makes an honest and valiant attempt to explain time crystals, especially when no one can really agree on the significance of such a discovery. I can tell you that this could ... maybe ... potentially ... possibly ... be responsible for more rapid growth of quantum computing. If you want to wade neck-deep into the physics of time crystals, you can read Google's scientific paper about them here (PDF). Material Can Convert Waste Heat To Electrical Energy  Have you heard of thermoelectric generators? Yeah, me neither. But, they are currently helping to power the Mars rovers by converting waste heat into electrical power. The problem is that the thermoelectric generators being used by the Mars rovers are quite expensive to manufacture. Research scientists, however, have found a way to make them much cheaper, according to an article in Science magazine. So the researchers looked at tin selenide crystals, which proved to be too costly to manufacture. They then looked at combining tin and selenium powders that, once heated and compressed, makes tin selenide crystals cheaply. Thermoelectric generators work by passing the heat from the hot side of the object through to the cool side, which sets up an electrical current. For example, if you put a thermoelectric generator on the exhaust manifold of a car, the side in contact with the exhaust manifold is the hot side, and the side farthest away from the exhaust manifold is considered the cool side. The movement of the otherwise wasted heat from the hot to the cold side sets up an electrical current, which can be used to power components, or that can charge a battery. Say Hello To The Windows 11 Linux Look-Alike 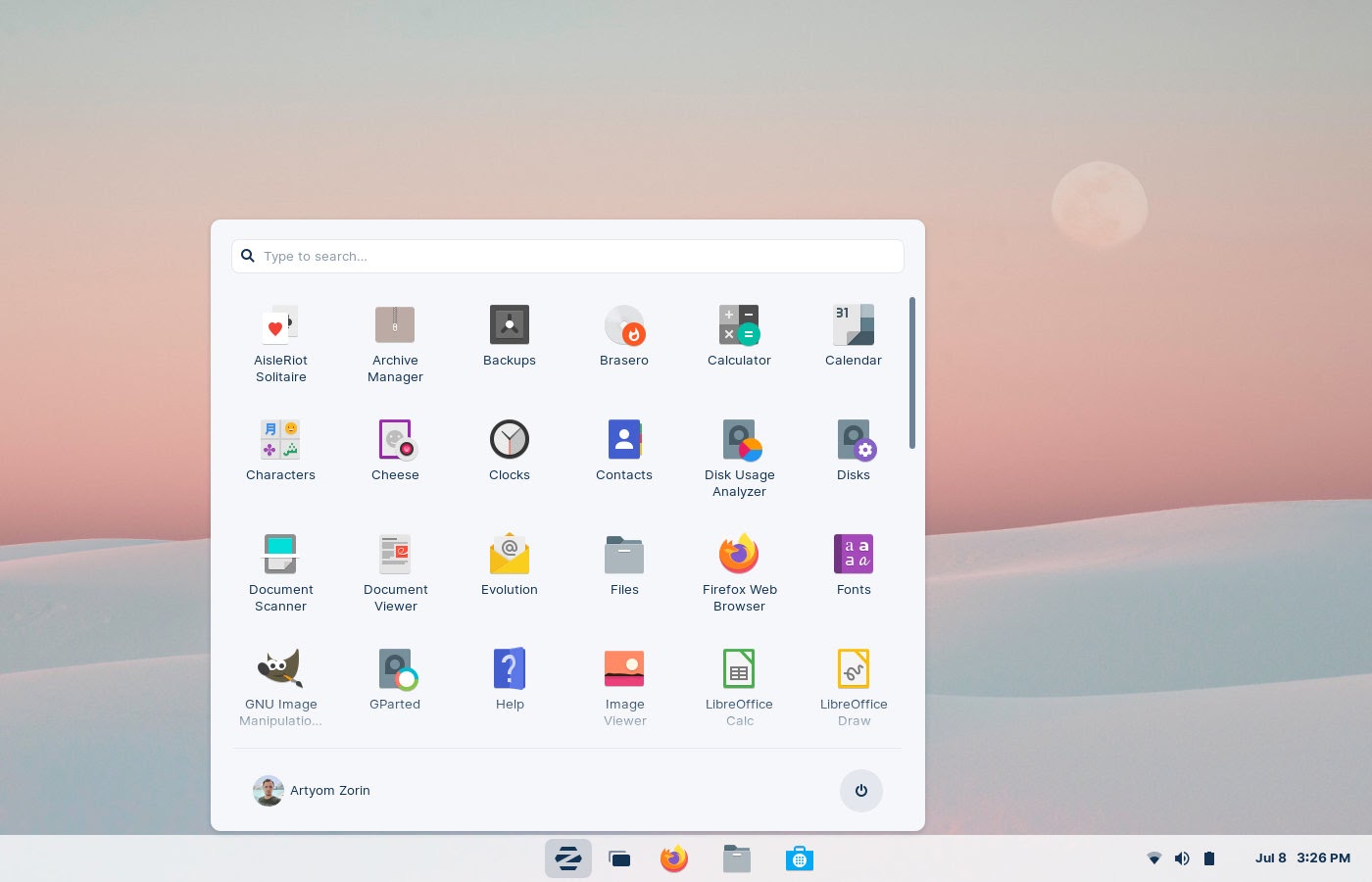 Zorin OS, a Linux distribution, has created a version for power users and professionals that looks like the upcoming Windows 11. The Win11 "window dressing" is only available to users who use the paid Zorin OS Pro version of the operating system. Its release is expected within the next few months. So, users can get the appearance of Windows 11, but the stability and security from running Linux. Zorin OS Pro comes with a full suite of productivity programs, such as GIMP, an Ebook reader, accounting software, 2D and 3D CAD software, a password manager, and much more. Purchasers of Zorin OS Pro will also have access to Zorin OS Pro Lite, a special version of the OS that is designed to run fast and stable on older computers. Paid users will also get access to Zorin Installation Support services, as well as helping to support the future of Zorin OS. Two Bicyclists Ride Their Own Tour de France, And Finish Ahead Of The Race Peloton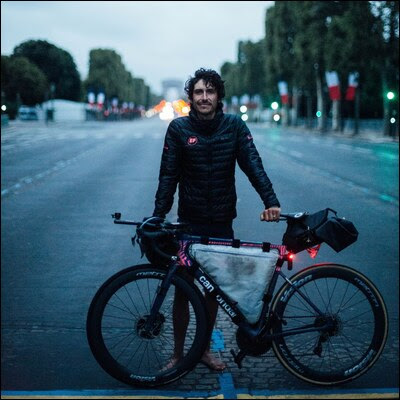  Lachlan Morton Photo: Rapha/Lucy Le Lievre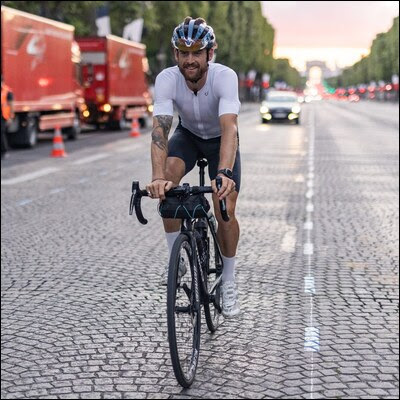  Jack "Ultra Jack" Thompson Photo: Tristan Cardew I don't talk about one of my favorite activities, bicycling, very much. But the accomplishments of these two bicyclists is, in my opinion, just mind blowing. First, on July 13, 2021, Bicycling magazine ran an article on Australian cyclist Lachlan Morton (top photo) riding his "Alt Tour" during the annual Tour de France bicycle race spectacular extraordinaire. Ok ... it's arguably the premiere bicycling race on the planet. Not only did Morton ride his "Alt Tour" completely self-supported without teammates, but also with no pursuit support vehicle, no soigneur, no chef, and no mechanic, AND he ALSO rode his bike from the end of one stage to the beginning of the next stage. To better visualize Morton's feat, this year's Tour de France's 21 stages was 3,414 Km (2,121 miles) long. With riding from the end of one stage to the beginning of the next, Morton's "Alt Tour" took him 5,510 Km (3,423 miles) to accomplish. He also climbed 23,000 more meters (75,459 feet) than the Tour de France competitors. Morton also skipped the two rest days that the competitors get, and rode at night as he needed to. Morton raised money with his "Alt Tour" to help donate 3,270 bikes to those in need. Meanwhile, Jack "Ultra Jack" Thompson (bottom photo above), also from Australia, also rode by himself to complete the entire Tour de France stages, as reported in Bicycling magazine on August 13, 2021. The 2021 Tour de France went from June 28 to July 18, with two off-days scheduled there for the competitors. Thompson started his personal Tour de France on July 5. His goal was to catch up with the Tour, pass them, and then stay ahead of them. Riding two stages a day (which meant pedaling for 13-14 hours a day on some days), he passed the Tour competitors on their rest day in Andorra. Thompson finished his personal Tour two days ahead of the actual Tour de France peloton, making the requisite traditional eight laps around the Champs-Élysées. Thompson differed from Morton in his approach, in that he had a support staff and a pursuit vehicle. After riding his two stages per day, he would often only get a few hours of sleep before it was time to start riding the next two stages. Even though I love bicycling, I'm not sure that I could do more than ONE stage of the Tour de France. These guys did the entire Tour de France, in fewer days than the Tour competitors. In my humble opinion, that is simply amazing. NASA Looking For Way To Kill ISS  NASA is looking at how to safely dispose of the International Space Station when the microgravity platform reaches the end of its lifespan, according to an article from United Press International. The United States started launching and assembling the space station in low earth orbit in 1998. The platform was projected to have a lifespan of 30 years. Those 30 years are up in 2028. The current plan, although not set in stone and has been tentative since its inception, has been on the table since 2010. It involves Russia launching one of its Progress service modules, and using the thrusters of that service module to start a controlled reentry for the space station. The 450-ton space station should mostly burn up in Earth's atmosphere, with remnants of engines, laboratories and living quarters falling into the Pacific Ocean. But, there's a possible snag in that plan. Russia has announced plans to withdraw from the ISS in 2024, and then possibly be completely done with it by 2025. That's well before 2028 when the space station's lifespan is finally up. So, NASA might not be able to rely on the use of Russia's Progress service module to fulfil the reentry plan as it's written right now. NASA might be forced to come up with an alternate plan that doesn't rely on the use of Russia's Progress service module. While they are looking at possibly using a SpaceX Dragon vessel, or Japan's H2-A vessel, the most likely candidate is Northrop Grumman's Cygnus cargo module as a replacement for the Russian module. PCLinuxOS Magazine Short Topix Roundup  SCIENTISTS HAVE FOUND A REMARKABLE LINK BETWEEN GUT HEALTH AND THE REVERSAL OF AGING, according to an article on Inverse. Researchers transplanted fecal matter from young mice into the GI tract of older mice. Afterwards, the older mice performed better on cognitive tests than they did previously. Upon dissection and studying their mouse brains, they discovered that the mice who received the fecal transplant had notable changes in the hippocampus of their brains, leading scientists to make the link between gut health (a healthy microbiome of the intestinal tract) and the effects of aging. THE NATIONAL CYBER SECURITY CENTRE IN THE U.K. (NCSC) RECOMMENDS USING THREE RANDOM WORDS FOR YOUR PASSWORDS, rather than the complicated mix of alphanumeric characters that most sites STILL recommend. I had to update a password on a site just the other day, and it had to have a mix of upper and lowercase letters, numbers, and a special character. One of the NCSC's most popular web pages, even five years after its initial publication, explains how choosing three random words can help users pick passwords that are easier to remember than the popular mixed passwords. It's those passwords that use the eclectic mix of alphanumeric characters that force users to pick weak passwords (like "pa55w0rd!"). The NCSC asserts that three random words are random enough to thwart the vast majority of hackers. Of course, as we've covered here in the pages of The PCLinuxOS Magazine many times before, the longer the password, the more secure it is. But, to be successful, the three words should be truly random, and not related to the other words in the passphrase. For example, the passphrase "horsecartontrapeze" (three random words off the top of my head, without spaces) would take 23 million years for a computer to crack, according to the "How Secure Is My Password" website. This is despite the lack of numbers, special characters, and using all lowercase letters. That sounds more than good enough to me! The length of reported time to crack the passphrase goes up exponentially as the length of the passphrase increases. RUSSIA HAS OFFERED TO HELP BOEING FIX THEIR STARLINER SPACE CAPSULE, according to an article on the Autoevolution website. In 2019, Boeing tested their Starliner capsule, but it failed to reach its intended target in orbit due to a software glitch. Then, after more than a year of trying to fix the issue, the next launch of the Starliner capsule never got off of the launchpad, when computers detected another problem, postponing the launch. Moreover, it's the way that the Russians voiced their offer to help, exposing that they are "well aware" of American engine building and all of their "developments." NETFLIX'S CAMPAIGN AGAINST USERS USING A VPN TO CONNECT TO THEIR SERVICES is also "ensnaring" regular, non-VPN using" customers in their castnet, according to an article on the How-To Geek website. While there are some VPN users who use a VPN to circumvent the geolocking of content, there are way more users who use a VPN to enhance their security and to help prevent unnecessary data collection on their online habits. So how do you know if Netflix is blocking your IP address, thinking you are using a VPN? Almost all of the content, except Netflix originals and a few miscellaneous bits of content have gone missing. If you find your IP address is being blocked by Netflix, you can contact Netflix customer service. Some users caught in this broad Netflix castnet have reported that asking for their ISP to assign them a new IP address has also resolved the issue. |

