| Previous
Page |
PCLinuxOS
Magazine |
PCLinuxOS |
Article List |
Disclaimer |
Next Page |
ICYMI: Use Netflix Secret Menu To Unlock New Movies |
|
by Paul Arnote (parnote)
 A remote worker hired by KnowBe4 as a software engineer on its internal IT team was actually a persona controlled by a North Korean threat actor, the security firm revealed in a blog post Tuesday, according to an article from Cyberscoop. Detailing a seemingly thorough interview process that included background checks, verified references and four video conference-based interviews, KnowBe4 founder and CEO Stu Sjouwerman said the worker avoided being caught by using a valid identity that was stolen from a U.S.-based individual. The scheme was further enhanced by the actor using a stock image augmented by artificial intelligence. An internal investigation started when KnowBe4's InfoSec Security Operations Center team detected “a series of suspicious activities” from the new hire. The remote worker was sent an Apple laptop, which was flagged by the company on July 15 when malware was loaded onto the machine. The AI-filtered photo, meanwhile, was flagged by the company's Endpoint Detection and Response software. Do you speak a second language (or more)? Do you want to learn a new language? Or do you want to brush up on a language you learned in the past, but don't use regularly enough to maintain fluency? Never fear, because Openculture.com has your back. They currently offer FREE language courses in 49 different languages (so far). You can learn more about the free courses from an article on Lifehacker. Are you tired of every streamer you subscribe to hiking prices year over year? Between endless price creep and crackdowns on password sharing, the modern streaming landscape is starting to look a lot like the old world of cable, according to an article from Lifehacker. On the other hand, there are a ton of free streaming options out there, and they're more enticing than ever. Here are 21 great sites and apps to turn to when you want something new to watch. (Note that many films are available on multiple free services at once, so if your selection has too many commercial interruptions or painfully low resolution on one source, search for it on another.)  Can't find anything good on Netflix? Try the secret menu to find movies and shows. The Netflix secret menu is your key to unlocking hundreds of new movies, says an article from CNET. Netflix is hiding things from you. There are hundreds more TV shows and movies on the streaming service than what you know. You aren't locked out of the content. You just need to learn how to use the Netflix secret menu. Only then will you unlock access to everything the service has available and more. Check out the article for all the juicy details. Running and cycling app Strava has a ton of features that help you find new running (and cycling) routes, including segments, the route builder, and the global heatmap. Earlier this summer, Strava began offering a weekly heatmap. It's great for finding trails and routes that are popular at a given time — but it may reveal information that is more private than what you thought Strava users could see, according to an article from Lifehacker. Using the weekly heatmap, the author was able to browse the map, select a neighborhood that looked like it had one active runner, and find that person's name and where they lived. To be clear, this person is a stranger to him, and he chose the neighborhood randomly. It took a matter of minutes to find this information. On July 30, 2024, OpenAI began rolling out an alpha version of its new Advanced Voice Mode to a small group of ChatGPT Plus subscribers, according to an article from Ars Technica. In early tests reported by users with access, Advanced Voice Mode allows them to have real-time conversations with ChatGPT, including the ability to interrupt the AI mid-sentence almost instantly. It can sense and respond to a user's emotional cues through vocal tone and delivery, and provide sound effects while telling stories. 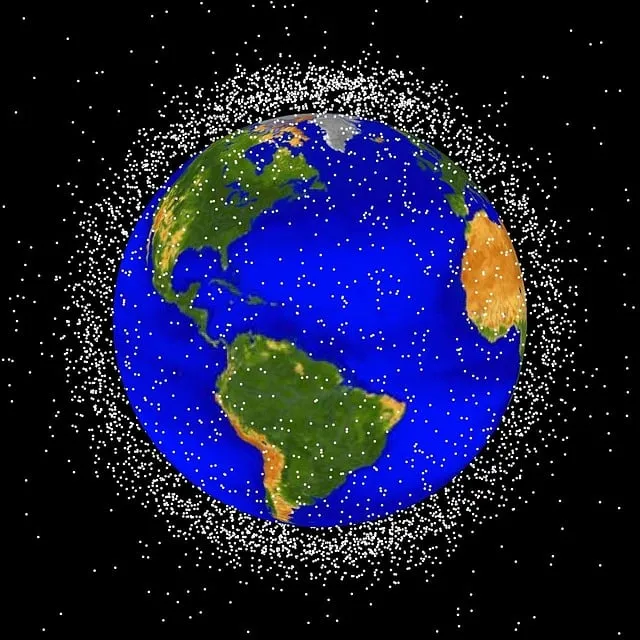 Image by WikiImages from Pixabay A space reconnaissance mission has returned unprecedented imagery of a metal hunk zooming around Earth, according to an article from Mashable. The discarded three-ton rocket, a robust piece of space junk some 36 feet (ca. 11 m) long, is the type of problematic debris agencies seek to remove from our planet's orbit. A future collision could spawn thousands more objects, posing threats to satellites and potentially the International Space Station. The Japanese satellite technology company Astroscale plans to remove this spent rocket stage, but is first gathering more information on the rocket's condition and motion. Thousands of accounts have been exposed after hackers used existing emails to create Google Workspace accounts and bypassed the verification process, according to an article from TechRepublic. According to Google, a “specially constructed request” could open a Workspace account without verifying the email. This meant that bad actors only required the email address of their desired target to impersonate them. While none of the fake accounts were used to abuse Google services, like Gmail or Docs, they were used to access third-party services through the “Sign in with Google” feature. Google Chrome users on Mac, PC, or Chromebook will soon see some new features designed to make searching the web more flexible, according to an article from TechRepublic. The new features are enabled by Google Gemini and other Google AI models. Google Chrome's last major AI update was in May, when it announced Gemini functionality across Workspace and added AI-generated answers to some Search queries. The three new features are: 1) Google Lens in Chrome on the desktop browser, 2) tab compare, an automatically generated comparison tool for online shopping, and 3) natural language search in browser history.  Image by InspiredImages from Pixabay Smart TV companies have injected ads into their platforms to play year-round, forcing you to dodge these promotions whenever you want to watch a show or movie. In researching how to stop these horror ads from popping up on my TV, there's one solution that seems to work well: blocking the domains from which the TV obtains the ads. While it is a little involved and doesn't apply to all brands (Vizio is one of the notable exceptions), it does appear to work for most Samsung, LG, and Roku smart TVs. If you have one of these TVs, and you're sick of these ads, too, give this a shot. Check out the article on Lifehacker to discover how to block these ads. Microsoft has confirmed the cause of the outage on July 30 was a distributed denial-of-service attack, according to an article from TechRepublic. However, its advisory added that the issue was exacerbated by an “error in the implementation of their defenses” during a mitigation attempt. The Azure cloud services were impacted between approximately 11:45 UTC and 19:43 UTC after being flooded by internet traffic. Redmond security pros say that the Azure Front Door and Azure Content Delivery Network components were “performing below acceptable thresholds, leading to intermittent errors, timeout, and latency spikes.” Microsoft has DDoS protection mechanisms that kick in automatically. However, an error in their implementation “amplified the impact of the attack rather than mitigating it.” The security team performed network configuration changes and failovers to alternate networking paths to provide relief to the primary systems. Google acted illegally to maintain a monopoly in online search, a federal judge ruled on August 5, 2024, a landmark decision that strikes at the power of tech giants in the modern internet era and that may fundamentally alter the way they do business, according to an article from the New York Times. Judge Amit P. Mehta of U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia said in a 277-page ruling that Google had abused a monopoly over the search business. The Justice Department and states had sued Google, accusing it of illegally cementing its dominance, in part, by paying other companies, like Apple and Samsung, billions of dollars a year to have Google automatically handle search queries on their smartphones and web browsers. “Google is a monopolist, and it has acted as one to maintain its monopoly,” Judge Mehta said in his ruling.  What happens now that Google has been declared a monopoly? That's exactly the question an article from Lifehacker takes a look at. In a historic blow to one of the biggest of big tech companies, the U.S. District Court for Washington, D.C. yesterday ruled that Google is a monopoly. In an opinion published August 5, 2024, U.S. District Judge Amit Mehta said the company has violated Section 2 of the Sherman Act, and declared that “Google is a monopolist, and it has acted as one to maintain its monopoly.” The focus is on its oldest business—search. Following revelations earlier this year that the company paid billions to make Google the default search engine on Safari and other browsers, the court decided that “Google's distribution agreements are exclusive and have anticompetitive effects.” The severity of the declaration means that Google probably can't just pay its way out of this one. If you remember the fallout from the antitrust case against Microsoft's Internet Explorer strategy in 2001, you've already got an idea of how this all could play out. One flu jab for all strains of the virus could be available within FIVE years following an “exciting” breakthrough, according to an article from Talker News. American scientists used a new vaccine platform to target the interior of the potentially deadly pathogen. They say the same method could be used against other mutating viruses, such as COVID-19, capable of triggering future pandemics. A universal flu vaccine would be effective against all human-adapted strains of influenza. On August 1, the EU Artificial Intelligence Act came into force across the bloc, setting strict rules on the use of AI for facial recognition, creating safeguards for general-purpose AI systems and protecting consumer rights to submit complaints and request meaningful explanations about decisions made with high-risk AI systems that affect citizens' rights, according to an article from TechRepublic. The AI Act legislation outlines EU-wide measures designed to ensure that AI is used safely and ethically, and includes new transparency requirements for developers of foundation AI models like ChatGPT. The European Union Parliament voted the Artificial Intelligence Act into law on March 13, 2024, with 523 members voting in favor of its adoption, 46 voting against it and 49 abstaining. The vote came after the member states agreed on the regulations in negotiations in December 2023.  Image by Ivana Tomášková from Pixabay Nearly three billion of us may have had our personal data exposed in an April hack, according to an article from Lifehacker. Seeing as there are just over eight billion people alive on the planet today, that means more than a third of the world's population may have been affected. As reported by Bloomberg Law, the exposure is the fault of Jerico Pictures Inc., operating as the background check company National Public Data, according to a lawsuit against the company. The suit alleges that, on April 8 of this year, the hacking group USDoD uploaded a database on the dark web site Breach Forums, called, simply, “National Public Data.” This 277GB database supposedly contained the information of 2.9 billion people. That data could be yours for the price of $3.5 million. A bid to break up Alphabet Inc.'s Google is one of the options being considered by the Justice Department after a landmark court ruling found that the company monopolized the online search market, according to people with knowledge of the deliberations, according to an article from Bloomberg. The move would be Washington's first push to dismantle a company for illegal monopolization since unsuccessful efforts to break up Microsoft Corp. two decades ago. Less severe options include forcing Google to share more data with competitors and measures to prevent it from gaining an unfair advantage in AI products, said the people, who asked not to be identified discussing private conversations. The team preparing NASA's X-59 continues through testing in preparation for the quiet supersonic aircraft to make its first flight, according to an article from SciTechDaily. This includes a trio of important structural tests and critical inspections on the path to flight. The X-59 is an experimental plane that will fly faster than the speed of sound without a loud sonic boom. It will be the first of its kind to fly, with the goal of gathering sound data for NASA's Quesst mission, which could open the door to commercial supersonic overland flight in the future.  National Institute on Aging, NIH New research from Emory University suggests that proteins accumulating around amyloid-beta deposits, rather than the deposits themselves, may play a crucial role in the progression of Alzheimer's disease, offering new directions for treatment, according to an article from SciTechDaily. Recent research from Emory University is prompting a reevaluation of current theories on the origins of Alzheimer's disease, a major cause of dementia globally. Led by scientists at the Goizueta Brain Health Institute, the team has uncovered compelling evidence that suggests a different mechanism may be responsible for Alzheimer's. In a paper published in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, Todd E. Golde and Yona Levites explain how the amyloid beta deposits long known to build up in the brains of Alzheimer's patients serve as a kind of scaffold for the accumulation of other proteins. Because many of these proteins have known signaling functions, their presence around the amyloid accumulations, known as plaques, could be the culprit causing brain cell damage rather than the amyloid itself. Along the coast of South Wales, renowned as a “prehistoric hotspot,” a mother and daughter made an extraordinary discovery: Camelotian footprints dating back a staggering 200 million years, confirming the presence of dinosaurs in Wales, according to an article from Interesting Engineering. The five footprints, each measuring an impressive 75cm (30in) apart, make humans look more like ants, and according to a paleontology expert at the National Museum Wales, it belonged to a “type of dinosaur called a sauropodomorpha” due to their immense size. Android updates often come with a bunch of security patches and bug fixes as standard, few of which ever get much attention, but the latest security update pushed out by Google is noteworthy: It addresses a vulnerability that may have already been exploited in the wild, which makes it even more important to update your devices as soon as possible, according to an article from Lifehacker. The vulnerability has been logged under the name CVE-2024-36971, and Google says it “may be under limited, targeted exploitation.” In other words, there's the possibility that hackers have already found ways to make use of it, albeit with limited end results or a limited number of devices affected. It's registered as a high severity remote code execution bug, which means it potentially enables someone else to run code on your device without your knowledge. While there's a very good chance you haven't been hit yet, you should keep an eye on security updates for your phone or tablet. Well-known Google bug squasher Clément Lecigne has been credited with discovering the problem.  MDEQ – via Facebook A fossil hunter in Mississippi recently unearthed an intact mammoth ivory 7 feet long, according to an article from Good News Network. Believing it was the tusk of a mastodon, a far more common proboscidean in the area, Eddie Templeton was nevertheless ecstatic to find one that wasn't fragmented. But it was only after scientists arrived from the Mississippi Museum of Natural History and were able to examine it that the real former owner of the tusk became clear. It was the ivory of a Colombian mammoth—the largest mammoth in North America, and rarely documented this far south. He has found mastodon teeth, jaws, saber-tooth cat gnashes, and other Ice Age treasures, but the size, majestic curl, and rarity of the ivory surely places it not only among the most remarkable finds of Templeton's career, but among the most remarkable in the state's history, as it's the first time an intact tusk from this species has been found in the Magnolia State. Amazon.com sued Nokia in Delaware federal court on Tuesday, accusing the Finnish telecom company of infringing a dozen Amazon patents related to cloud-computing technology, according to an article from Reuters. Amazon said in the lawsuit that Nokia misused Amazon Web Services (AWS) technology related to cloud computing infrastructure, security and performance to bolster its own cloud offerings. Nokia said in a statement that it would “review these matters and defend ourselves vigorously in court.” An Amazon spokesperson declined to comment. An unexplored region in the foothills of the Southern Pyrenees in Spain is shedding light on a little-known period of Neanderthal history, according to an article from SciTechDaily. New research from The Australian National University (ANU) suggests that this area could offer valuable clues to help archaeologists unravel the mystery of the Neanderthals' decline. Abric Pizarro is one of only a few sites worldwide dating from 100,000 to 65,000 years ago during a period called MIS 4. The researchers have gathered hundreds of thousands of artifacts, including stone tools, animal bones, and other evidence, providing significant data about the Neanderthal way of life during that time — largely unknown in human history until now. The findings reveal Neanderthals were able to adapt to their environment, challenging the archaic humans' reputation as slow-footed cavemen and shedding light on their survival and hunting skills.  Image by Alexandra_Koch from Pixabay Isn't It Ironic? Google researchers have come out with a new paper that warns that generative AI is ruining vast swaths of the internet with fake content — which is painfully ironic because Google has been hard at work pushing the same technology to its enormous user base, according to an article from Futurism. The study, a yet-to-be-peer-reviewed paper spotted by 404 Media, found that the great majority of generative AI users are harnessing the tech to “blur the lines between authenticity and deception” by posting fake or doctored AI content, such as images or videos, on the internet. The researchers also pored over previously published research on generative AI and around 200 news articles reporting on generative AI misuse. Google is denying online reports that it is ending the Fitbit brand, and a representative says that the company has new Fitbit-branded products in the pipeline, according to an article from CNET. A spokesperson for Google, which purchased Fitbit in 2019, told CNET in an email, “We are very committed to Fitbit, and even more importantly to the customers that use and depend on those products and technology.” According to a report from the site TechRadar, Google “quietly confirmed” that it will no longer produce Fitbit Versa or Sense smartwatches. This comes as Google just rolled out its Pixel Watch 3 smartwatch, which Google says incorporates some of Fitbit's technology. According to the TechRadar report, Fitbit's trackers -- the Inspire, Luxe and Charge -- will still exist, but the implication is that five years after announcing it was buying Fitbit for $2.1 billion, Google is phasing out the brand. Google insists this is not the case. UPDATE: Well, that didn't last long. Google has confirmed that Fitbit as a brand will no longer be making new smartwatches, with the Pixel Watch series taking over that form factor going forward, according to an article from 9to5google. Google has quietly made its latest text-to-image AI model, Imagen 3, available to all U.S. users through its ImageFX platform and published a research paper detailing the technology, according to an article from Venture Beat. This dual release marks a significant expansion of access to the AI tool, which was initially announced in May at Google I/O and limited to select Vertex AI users in June.  Image by RoadLight from Pixabay A new attempt to predict earthquakes with the aid of artificial intelligence has raised hopes that the technology could one day be used to limit earthquakes' impact on lives and economies, according to an article from SciTechDaily. Developed by researchers at The University of Texas at Austin, the AI algorithm correctly predicted 70% of earthquakes a week before they happened during a seven-month trial in China. Researchers at the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST) in Saudi Arabia have achieved a significant breakthrough in developing optical lenses for mobile phone cameras, according to an article from Interesting Engineering. They have created a cutting-edge AI model specifically designed to aid in developing these lenses. According to the researchers, an automated computational approach to the optical lens design of imaging systems promises to provide optimal solutions without human intervention, slashing the time and cost usually required. The result could be improved cameras for mobile phones with superior quality or new functionality. The European Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (ESMC), a new microchip manufacturing plant to be built in Dresden, Saxony, will be the first to produce so-called high-performance chips in the EU, European Commission president Ursula von der Leyen said during a visit to the nascent plant on August 20, according to an article from Euro News. “This new centre qualifies under the European Chips Act as a first-of-a-kind facility. It will manufacture products that are not present or planned in any other facility across Europe. That means this facility is also entitled to national financial support,” Von der Leyen said, adding that the European Commission has approved a €5 bn German measure to support ESMC in the construction and operation of its plant. The new plant will produce so-called high performance chips, using field-effect transistor (‘FinFET’) technology and allowing the integration of several additional features in one chip. The produced chips will offer better performance while at the same time reducing total power consumption. ESMC – a joint venture between Taiwan Semiconductor Manufacturing Company (TSMC), Bosch, Infineon, and NXP – is planned to be operating at full capacity by 2029, and is expected to produce 480,000 chips – used for automotive and industrial applications.  Cresilon, Inc. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved a novel treatment that is designed to stop severe bleeding in a matter of seconds, according to an article from Fox News. TRAUMAGEL — made by Cresilon Inc., a Brooklyn-based biotechnology company — is a plant-based hydrogel that comes in a pre-filled syringe, according to a press release. First responders, paramedics, and combat medics can use the gel to rapidly stop severe blood loss from wounds due to gunshots, stabbings or other traumatic events. Joe Landolina, Cresilon's CEO and co-founder, invented the gel in his dorm room when he was a 17-year-old chemical and bioengineering student at NYU. TRAUMAGEL, which is “the color and texture of hummus,” works by instantly creating a mechanical barrier against bleeding at the site of the wound, Landolina said. “That barrier then allows the patient to quickly produce their own natural clot that doesn't become incorporated with TRAUMAGEL, allowing TRAUMAGEL to then be removed without disturbing the clot.” The gel is supposed to be removed within 24 hours. WHO Director-General Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus has determined that the upsurge of mpox in the Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC) and a growing number of countries in Africa constitutes a public health emergency of international concern under the International Health Regulations, according to a news release from the WHO (World Health Organization). Dr Tedros's declaration came on the advice of an IHR Emergency Committee of independent experts who met earlier in the day to review data presented by experts from WHO and affected countries. The Committee informed the Director-General that it considers the upsurge of mpox to be a PHEIC, with potential to spread further across countries in Africa and possibly outside the continent. According to an article from Live Science, the Milky Way galaxy has a 50-50 chance of colliding with a nearby galaxy in the next 10 billion years, a new study finds. Yet while those odds appear daunting, the new finding suggests the catastrophic collision is far less likely than previously thought. Located roughly 2.5 million light-years away, the Andromeda (M31) galaxy is approaching our Milky Way at a speed of 68 miles per second (110 kilometers per second). Because of this, astronomers have long predicted that the two galaxies will inevitably become locked in a fatal dance sometime in the next several billion years — spiraling into each other and merging to form a new galaxy. But according to a new study, published July 31 on the preprint server arXiv, the two galaxies are just as likely to narrowly miss each other. “We find that uncertainties in the present positions, motions, and masses of all galaxies leave room for drastically different outcomes, and a probability of close to 50% that there is no Milky Way-Andromeda merger during the next 10 billion years,” the authors wrote in the study.  Another month, yet another set of Google Chrome vulnerabilities. If you use Google Chrome or a Chromium-based web browser, you need to update it ASAP, according to an article from Lifehacker. Google's latest update for Chrome, version 128.0.6613.84/.85 (Windows/Mac) and 128.0.6613.84 (Linux), comes with patches for 38 security vulnerabilities, eight of which Google identifies as “High” severity. Google detailed all these patches in its latest Chrome Releases blog post, running through each vulnerability's type, severity, reward (the money rewarded to the researcher who discovered it), and noting who reported the flaw. One of those is a zero-day vulnerability that has been exploited “in the wild.” From an article by ADWEEK, sales representatives from Google have suggested that advertisers target teenagers on YouTube, seemingly in violation of the platform's own policies, according to three ad buyers and written documentation seen by ADWEEK. This activity goes beyond the practice that was first identified by Financial Times earlier this month. Earlier this month, FT (Financial Times) reported that Google worked with Meta to target 13- to 17-year-old YouTube users with ads, targeting a group of users labeled as “unknown”—a group that Google knew was skewed towards under-18-year-olds, the article said. But buyers told ADWEEK that this activity involves more advertisers than the special arrangement between Meta and Google identified by FT. All buyers who spoke to ADWEEK for this article did so anonymously to discuss sensitive industry relations, but their identities are known to ADWEEK. A newly discovered bug causes iPhones and iPads to briefly crash. All you need to trigger the bug are just four characters, according to an article from TechCrunch. On August 21, 2024, a security researcher found that typing “”:: can cause the Apple mobile user interface, called Springboard, to crash. TechCrunch verified that those characters do crash Springboard when typed into the Search bar in the Settings app, as well as if you swipe all the way to the right on your home screen and type them into the App Library search bar. |